As link building becomes a more cautionary practice it’s necessary to get a clear idea of how to acquire the best links for your website, in light of this guest blogging in 2020 can be a good method.
Although Google has openly placed more scrutiny on guest blogging, there is undoubtedly still value in acquiring a link from a recognizable high-authority site in your niche. That being said, it’s not easy to secure links from top sites-especially when you need to scale up your efforts. Many sites only offer nofollow links and with growing competition, there is no shortage of good writers to populate these blog sites with high-quality articles.
This doesn’t mean that all hope is lost in the world of guest blogging. It just means your efforts need to be planned and strategized. Here are some top tips to get the most out of your guest blogging in 2020.
- Create a master list of guest blogging sites
- Qualify relevance
- Qualify authority
- Check search visibility
- Combine outreach tactics to land opportunities
- Research your target sites blog
- Strategize your topic
- Create an enticing storyline with your headings
- Submit infographics
- Make your links count
1. Create a master list of guest blogging sites
Be extremely organized with your approach to guest blogging to streamline the process. Create a master list on a spreadsheet in order to keep track of your efforts. Record the sites you’ve made contact with, the dates you’ve submitted articles or pitches and any notes on the efforts you’ve made to help you avoid duplicate efforts.
Start with a pre-existing list
There are dozens of sites that have created a list of the top guest blogging sites for multiple industries. You can start your master list with the most popular authority sites in your niche by exploring a few pre-existing lists.
A few examples that offer a list of guest blogging sites are Lilach Bullock, Izideo, Advanced Web Ranking, and Solvid. This will start you off with a solid base of top sites to work from that are well known within your niche.
Scrape Google
It’s impossible to know about every website that offers guest blogging without doing some background research. One method of discovery is to use command operatives to scrape Google.
Use the following commands paired with a keyword to find guest blogging sites:
- “inurl” will tell Google to look for keywords in the URL
- “intitle” will find sites with the keyword in the title
Mix and match commands to produce different results:
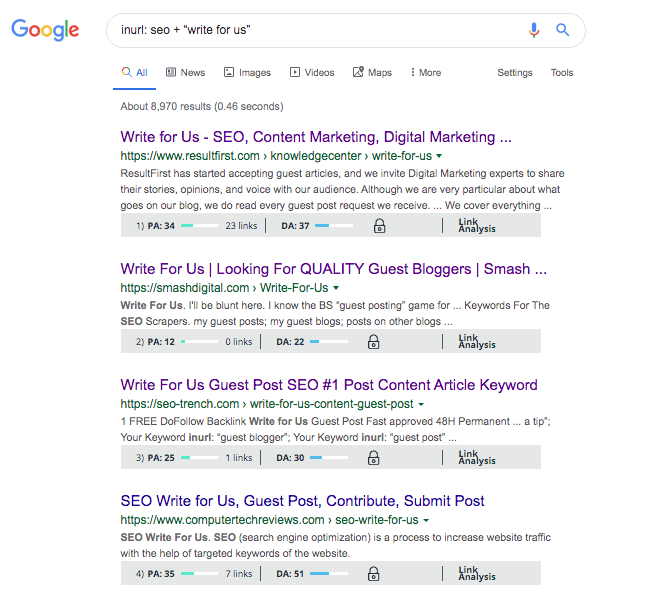
Inurl: “digital marketing” + “write for us”
Intitle: SEO + “guest post”
Check out guest post sites from your competition
It’s no secret that you can use any backlink report to get the inside scoop on the strength of your competitions backlink profile. Use Moz, SEMRush, Ahrefs or any tool of your choice to produce to see what links your competition has acquired. In the digital marketing space, a typical backlink profile will yield a number of guest blogging sites your competition found in which you can also submit an article.
2. Qualify relevance
If there were no authority transferred by links, what sites would you link to? This type of approach to link building will help you seek out the sites that are highly relevant to your website without being blinded by domain authority.
It happens quite often that at first glance a website DA will influence your perception of the quality of the link which is not always an accurate indication of whether that link will benefit your site.
Make sure the website you are submitting to is in your niche or a direct vertical. Confirm they are publishing content similar to yours so that a clearly defined relationship can be established that indicates relevance to your content.
3. Qualify authority
The DA of a site is the first indicator of a quality link. Although it doesn’t provide the entire picture of what makes up a quality link, you can use this indicator to prioritize your submission sites.
Use the Mozbar for a quick view of a website’s metrics before making a submission.
Target sites that will have a positive impact on your authority. Certain keywords will require links from higher DA sites and others you can get away with links from lower DA sites.
4. Check search visibility
The search visibility of a website indicates how well the site is performing by ranking for keywords and driving traffic. A site that has good metrics won’t necessarily be a good link if it doesn’t have any visitors reading its content.
The authority gained from a link is an important aspect of link building, but the overarching goal behind the practice is to build streams of relevant traffic and awareness of your website.
5. Combine outreach tactics to land opportunities
Not every site will advertise that they accept guest posts but that doesn’t mean they won’t be happy to publish some great content you’re offering. Adam Envoy was able to secure 8 DA60+ sites in 15 days in his guest-posting project and attributed a portion of his success to targeting site owners with an outreach email before proposing a guest post.
Use LinkedIn and Facebook to make initial contact with content managers and editors and let them know you’re interested in link building and guest blogging. In most cases, you will get a response that will lead you to the right person and a link building opportunity.
Even if you don’t get the desired response, making contact is the first step in building a mutually beneficial relationship further down the line.
6. Research your target sites blog
One of the top reasons why site owners don’t respond to an outreach email is because “They didn’t read my blog”. Get a feel for the type of content they’re publishing by scanning through titles and reading relevant content. You can pick up on trends and characteristics that will make your pitch much more targeted to your prospect’s website.
7. Strategize your topic
Choose a topic that hasn’t been covered in-depth on your prospects’ blog. This presents more value for a blog owner to be presented with the option of adding content their site is lacking.
The topic you choose to write about should be something suited to your strength. Apart from making a list-style article, dive deep into a relevant topic that can be broken down and optimized for a specific keyword topic. Writing optimized SEO content is a bonus for publishers when the article is already primed and ready to rank.
8. Create an enticing storyline with your headings
Most online readers are scanners by nature, in fact, 43% of people admit to skimming through articles when they read them. which is a trait you can capitalize on with an original title and descriptive subtitles. Your outline should reflect a storyline that clearly describes the content of your article.
The first impression of your article an editor (and their audience) will have is the headline of your proposed article. This should clearly convey to the reader what they will get from reading your post and how will it will benefit them. Use headline strategies that are proven to improve click-through rates by appealing to the various types of readers.
Follow up the headline with your main points emphasized as subtitles. Make your article actionable and complete for a person who scans through your content.
9. Submit infographics
Although the numbers will show that infographics peaked in 2014 and 2015, they are still an effective means of creating backlinks. In many cases, infographics receive exceptional consideration as a guest post because publishers know that the potential to attract backlinks improves tremendously.
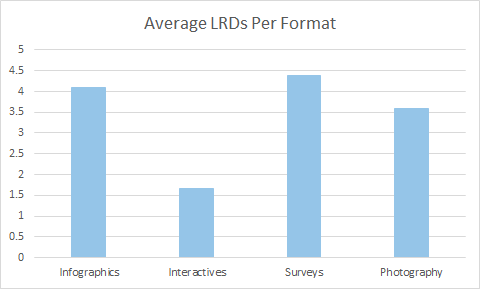
Image source: Moz
Use an infographic tool from companies like Venngage, Visme or Piktochart to add more appeal to your article submissions.
10. Make your links count
The links you insert in your article should provide value to the reader by taking them somewhere that enhances their understanding of a particular point or topic.
Contextual links are more valuable than the link in the author’s box. Make sure to give yourself a link to content that is relevant to your article. Avoid being overly self-promotional by making sure the links you give yourself are truly beneficial to the reader.
Keep in mind excessive anchor text to the same page will result in a negative effect on your ranking. Mix up your links to appear natural with a brand link, long-tail, and naked URL wherever applicable.
Promote previously published articles
Link to previously published articles to increase the DA of those pages and create more powerful links to your site.
Linking to articles you’ve published is less conspicuous than linking to your own site, which gives you more leeway in the number of links you create.
The value of your work as a future guest author increases when site owners see you link to your published work thereby promoting their site as well.
Link to prospects and influencers
Make it a point to link to the people who are in a position to help you in your backlinking strategies. Separate yourself from the masses by showing an influencer quality links you’ve sent to their work. Keep track of the links you accumulate and make it part of your outreach strategy to build powerful alliances and partnerships.
Enjoy the benefits of guest blogging
There is no doubt that despite the scrutiny placed on guest blogging by Google, it is still one of many effective methods of link building.
A well-executed strategy will provide your site targeted referral traffic as well as improved authority and ranking ability. Use guest blogging opportunities to brand your business, demonstrate thought leadership and build mutually beneficial relationships through your link building efforts in 2020.
Christian Carere is an avid contributor to the digital marketing community and a social media enthusiast. He founded Digital Ducats Inc. to help businesses generate more leads and new clients through custom-designed SEO strategies.
The post 10 Tips for improved guest blogging in 2020 appeared first on Search Engine Watch.
from SEO – Search Engine Watch https://ift.tt/2QBybOK
via IFTTT