Here’s a bold statement: “SEO in the travel industry is immensely challenging.”
The sheer number of pages to manage, complexities of properties, flights, accommodation, availability, occupancy, destinations, not to mention the crazy amount of APIs and databases to make a travel site function, can all make life tricky for an SEO, particularly when it comes to the development queue…

Having said that, there are still common mistakes and missed opportunities out there that have the potential to be really impactful and believe it or not, they don’t actually require a huge amount of resource to put right.
So, here’s a list of the six most common travel SEO mistakes to get right for 2019:
-
Forgetting about index bloat
There are a LOT of facets and filters when it comes to commercial travel category pages, arguably the most of any industry.
Typically with every facet or filter, be it; availability, location, facilities, amenities nearby, occupancy etc. A URL is created with the associated parameters selected by the user.
If not handled correctly, this can produce thousands of indexable pages that have no unique organic value to users.
This is a problem for a number of reasons:
- It can be confusing for search engines because they can find it tricky to identify the best and most relevant URL to rank and show users depending on their query
- It can dilute domain level ranking signals drastically
- It can cause a huge amount of duplicate content issues
- It can waste crawl budget which for big travel sites is super important
Combined, this can cause big losses in rankings, traffic and subsequently conversion!
How to identify index bloat
Go to Search Console (formerly Google Webmaster Tools) and check your ‘Index Coverage’ report or, in the old version, check ‘Index Status’ to see if you can see any spikes or growth in ‘Total Indexed’ pages. If you notice something like the graph below and it’s not expected, then there may be a problem:
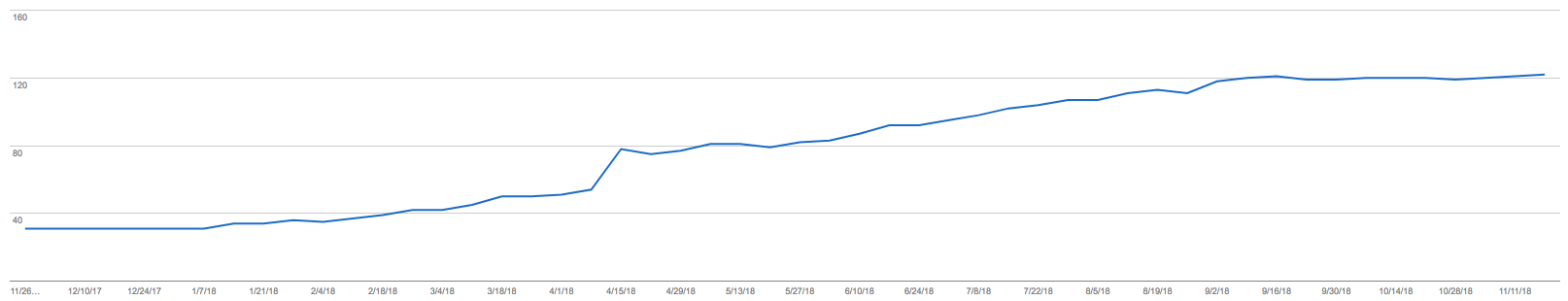
If you find there is a big increase and you can’t explain why, conduct some ‘Site:’ operator searches and spot check areas of your site where this may be commonplace to see what you can find.
Here’s an example of index bloat from the page speed tool ‘Pingdom’. It seems as though every input a user executes produces an indexable URL:
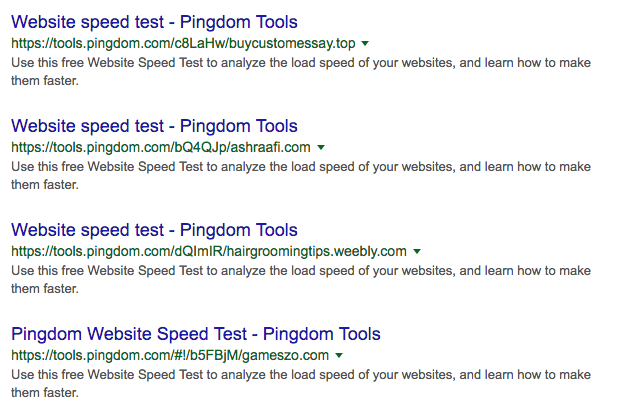
Once you’ve found a problem like this, review the extent of it with a Screaming Frog crawl. This way you can see how many URLs are affected and distinguish between whether they are actually indexable or not.
For example, there may be a few hundred pages that are indexable but have not yet been found and indexed by Google.
How to fix index bloat:
- Noindex – Use a page level meta ‘noindex’ directive on the culprit pages
- Where possible redirect – index bloat can happen as a result of mountains of historical 404 pages too, 301 redirect them into the most appropriate page to consolidate
- Canonicalisation – apply an absolute canonical tag to the culprit pages to indicate that they are duplicate
- Pagination – where possible use rel=”next” & rel=”prev” markup to show that pages are part of a series
- URL parameter tool – By far the easiest but arguably the most risky method is using Google’s parameter handling tool to indicate the purpose of the culprit pages, be careful though, this can cause bigger problems if implemented incorrectly
Expert tip
If any of the above are difficult to get implemented in your dev queue and you don’t trust yourself using the parameter handling tool, you can actually noindex web pages & directories in your robots.txt file. You can actually add lines reading:
Noindex: /directory/
Noindex: /page/
This could save you a lot of time and is fully reversible, so less risky if you have control over your robots file. If you’ve never heard of this, don’t worry it is supported and it does work!
-
Unemotive meta titles
It’s pretty staggering but in the UK, there’s a lot going on in January for travel — it is certainly the biggest spike in the year for many brands, followed by ‘holiday blues’ peaks after summer.
Here’s the trend of interest over time for the query ‘tenerife holidays’ (a destination famed for its good weather all year round) to show you what I mean:
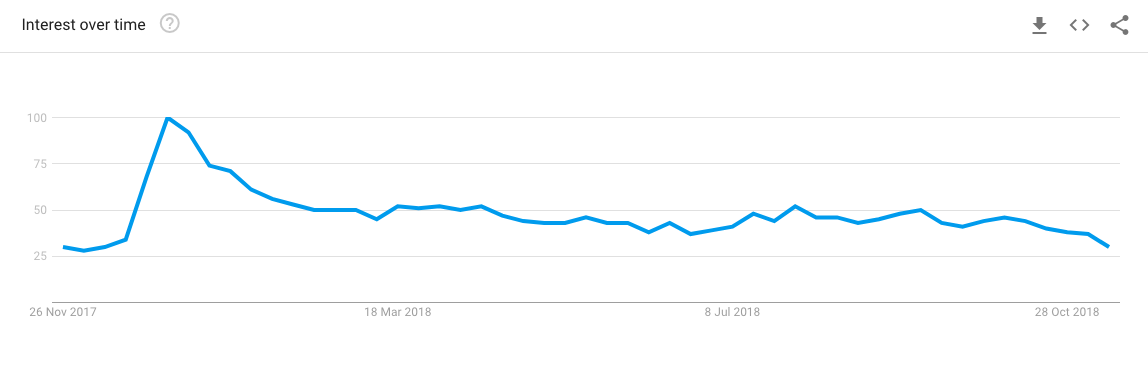
January might be a bad time to experiment because of the higher interest but, the rest of the year presents a great opportunity to get creative with your titles.
Why would you?
Simply, keyword heavy titles don’t inspire high click-through rates.
Creative titles entice users into your landing pages, give your brand a personality and increase your click-through rate. This sends strong positive relevancy signals to Google which helps towards highlighting that your website is the best for the initial user query.
Here are a few things you can try with supportive content and commercial landers:
- Get emotional, people buy holidays on the experiences they anticipate having. Play on that with your titles – how will products/content from this page make the user feel?
- Where possible use a numbered list to be as descriptive as possible
- Use strengthening words such as premium, secret, amazing, proven, guaranteed
- Tie in emotional hooks using words like; fun, adventure, seamless, safe, welcoming, luxury, relaxing
- Experiment with ‘price from’ and actually quote pricing in the title
- Switch up your ‘PHP’ generated title tags for property pages and experiment with more descriptive wording and not just PROPERTY NAME | LOCATION | BRAND – but don’t remove any keyword targeting, just improve those titles.
Expert Tip
Write five completely unique title tags for the same page and test each one with a Facebook or PPC ad to see whether they outperform your current iteration in terms of engagement.
-
Poor merchandising
As previously mentioned, the travel industry experiences peaks and troughs of consumer behavior trend throughout the year which causes the majority intent to switch dramatically across different months in the year.
So, having a deep understanding of what users are actually looking for is really important when merchandising high traffic pages to get the best conversion out of your audience.
In short, gaining an understanding of what works when, is huge.
Here’s some tips to help you make better merchandising decisions:
- Use last year’s email open rate data – what type of content/product worked?
- Use Google Search Console to find pages that peaked in organic traffic at different times
- Involve the social media team to get a better understanding of what your audience is engaging with and why
- Use Google Trend data to verify your hunches and find clearer answers
- Use UGC sites such as Quora to find questions users are asking during different months of the year. Use the following site operator and swap out ‘holiday’ for your topic: ‘site:quora.com inurl:holiday’ and then filter by custom date range on your search
Often consumers are exposed to the same offers, destinations and visuals on key landing pages all year round which is such a missed opportunity.
We now live in a world of immediacy and those in the industry know the challenges of users cross-shopping between brands, even those who are brand loyal. This often means that if users can’t find what they are looking for quickly, they will bounce and find a site that serves them the content they are looking for.
For example, there’s an argument for promoting and focusing on media-based content, more so than product, later in the year, to cater to users that are in the ‘consideration’ part of the purchasing funnel.
Expert tip
Use number five in this list to pull even more clues to help inform merchandising
-
Holding back on the informational market share
I grant you, this is a tall order, travel advice, blogs and guides are a standalone business but, the opportunity for commercial travel sites to compete with the likes of TripAdvisor is massive.
An opportunity estimated from our recent Travel Sector Report at 232,057 monthly clicks from 22,040 keywords and only Thomas Cook is pushing into the top 10.

Commercial sites that don’t have a huge amount of authority might struggle to rank for informational queries because dedicated travel sites that aren’t directly commercial are usually deemed to provide better/unbiased content for users.
Having said that, you can see clearly from above that it IS possible!
So, here’s what you should do…
…focus on one thing and do it better than anyone else
Sounds pretty straightforward and you’re probably thinking ‘I’ve heard this before’ but, only a handful in the travel industry are actually doing this well.
Often you see the same information from one travel site to the next, average weather, flight times, the location of the country on a map, a little bit of fluff about the history of the destination and then straight into accommodation.
This is fine, it’s useful, but it’s not outstanding.
Let’s take Thomas Cook as an example.
Thomas Cook has built a network of weather pages that provide live forecasts, annual overviews as well as unique insights into when is best to go to different destinations. It even has a tool to shop for holidays by the weather (something very important to Brits) called ‘Where’s Hot When?’

The content is relevant, useful, concise, complete, easy to use, contemporary in design and, most importantly, better than anyone else’s.
In short, Thomas Cook is nailing it.
They have focused on weather and haven’t stopped until it’s as best as it can be.
Why did they bother with weather? Well it’s approximately a third of all travel-related informational searches that we found in our keyword set from the Travel Sector Report:
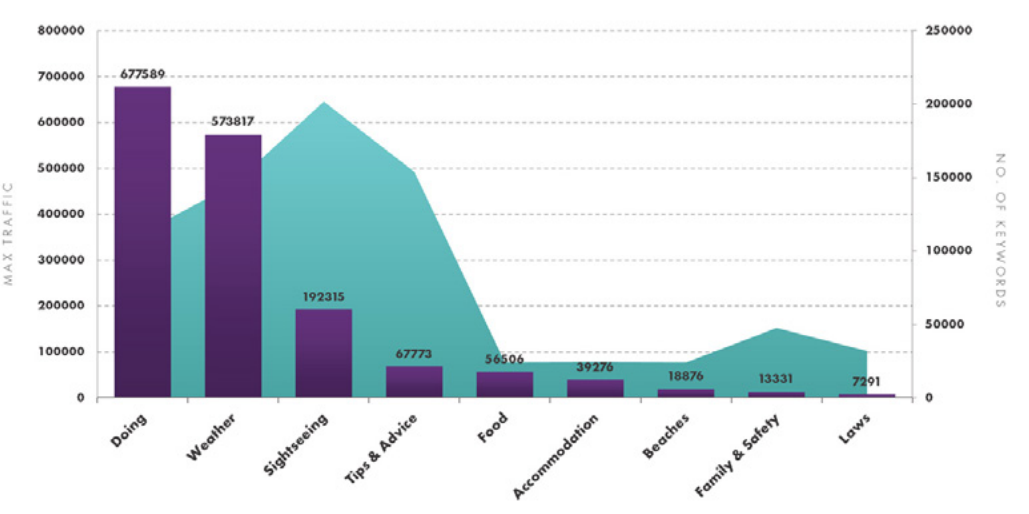
Apply Thomas Cook’s methodology to something that is relevant to your audience, it could be; family attractions, adult only tour guides, Michelin star eateries, international laws families should be concerned about, the list is plentiful!
Find something, nail it.
-
Ignoring the gold in on-site search
There are some big travel sites out there that don’t have an on-site search function which is a huge missed opportunity. Travel sites are inherently difficult to navigate with such a volume of pages, site search is quite often a great solution for users.
As well as this, it can give marketers some amazing insight into what users are looking for, not just generally in terms of the keywords users might be using but also the queries users are searching on a page by page level.
For example, you could drill down into the differences between queries searched on your homepage vs queries searched on specific landing pages to spot trends in behavior and fix the content gaps from these areas of the site.
You could also use the data to inform merchandising decisions to address number three on this list.
In doing this, users are actually telling you exactly what they are looking for, at what time, whether they are a repeat visitor or a new one and where they’ve come from to visit your site.
If you spend the time, this data is gold!
If you can’t get buy in for this, test the theory with an out of the box search function that plugs straight into your site like searchnode. Try it for six months, you might be surprised at how many users turn to it and you will get some really actionable data out of it.
It’s also super easy to track in Google Analytics and the reports are really straightforward:
1. Go to Admin
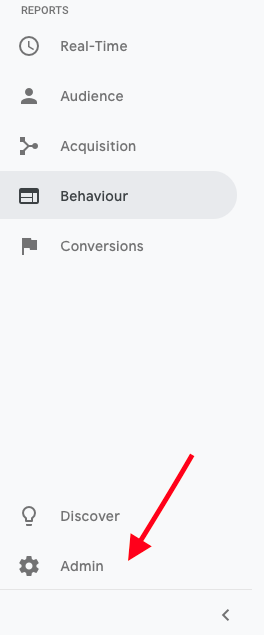
2. Click ‘View Settings’
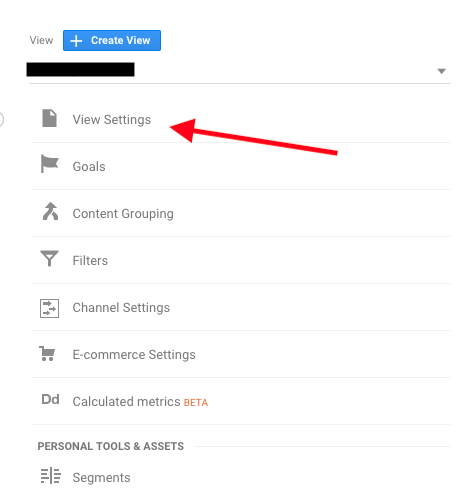
3. Switch ‘Site search Tracking’ on
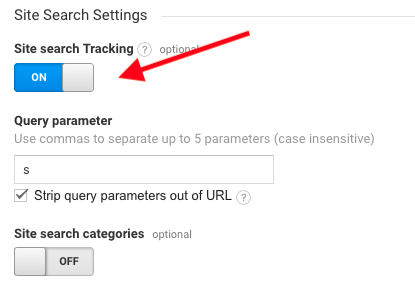
4. Strip the letter that appears in your site’s search URL before the search terms e.g. for wordpress this is usually the letter “s”: www.travelsite.co.uk/?s=search-term
5. Click ‘save’, boom you’re done.
Let Google collect data, extract it monthly and dig, dig furiously!
-
Ignoring custom 404 errors pages
Who doesn’t love a witty 404 page. More and more often you’ll find that when webmasters optimize a 404 error page they make them lighthearted. Here’s a great example from Broadway Travel:

There is a reason why webmasters aim for a giggle.
Think about it… when users hit a 404 error page, 100% of the time there’s a problem, which is a big inconvenience when you’re minding your own business and having a browse, so, something to make you laugh goes a long way at keeping you unfrustrated.
Time to name names, and show you some 404 error pages that need some work…
British Airways
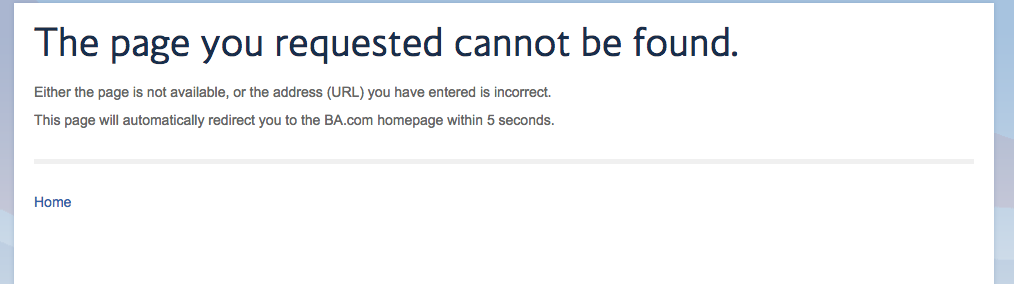
TUI & Firstchoice

Expedia

Momondo
404 error pages happen over time, it’s totally normal.
It’s also normal to get traffic to your 404 error page. But it’s not just any old traffic, it’s traffic that you’ve worked hard to get hold of.
If, at this point, you’re thinking, ‘my site has recently been audited and internal links to 404 pages have been cleared up’.
Think again!
Users can misspell URLs, ancient external links can point to old pages, the product team can make mistakes, as meticulous as you may be, please don’t discount this one.
Losing quality users because of a bad 404 experience is an SEO’s idea of nails down a chalkboard.
Here are some tips to optimize your 404 pages:
- Hit them with something witty but don’t be controversial
- Feature the main site query forms prominently so users can conduct another ‘base’ search
- Feature a site search option as well – an error page is a perfect opportunity to get users to conduct a site search to give you some insight into what they are looking for (number five on this list)
- Include curated links to most popular top level pages such as destinations, guides, hotels, deals etc. This will allow users to start from at the top of each section and it will also allow search engines to continue crawling if they hit a 404 page
- Re-emphasize branding, USPs, value proposition and trust signals to subconsciously remind users of why they’re on your site in the first place
Even if you think your 404 is awesome don’t neglect them when they pop up:
- Review the 404 page data in Google Analytics behavior flow to find broken links you may not have known about and fix them
- Keep on top of your 404 pages in Google Search Console and redirect to appropriate pages where necessary
404’s are often the bane of an SEO’s life and you might think about ways to get out of keeping on top of them.
Sadly there aren’t any short cuts….
…Bonus SEO mistake
Creating a global 301 redirect rule for every 404 page and direct them to your homepage.
This is surprisingly common but is poor SEO practice for a number of reasons, firstly you won’t be able to identify where users are having issues on your site when 404 pages pop up.
You may also be redirecting a page that could have originally had content on it that was totally irrelevant to your homepage. It’s likely in this situation that Google will actually override your redirect and classify it as a soft 404, not to mention the links that may have originally pointed to your 404’s.
Save your users, build a 404 page!
Final thoughts
No site is perfect, and although it might appear as though we’re pointing fingers, we want you to be able to overcome any challenges that come with SEO implementation — there’s always a bigger priority but keep your mind open and don’t neglect the small stuff to stay ahead of the game.
The post Six most common travel SEO mistakes to get right in 2019 appeared first on Search Engine Watch.
from SEO – Search Engine Watch https://ift.tt/2zWz2lS
via
IFTTT